Research Information
- Particulate Matter
- CAPSS
- SEMS
Home > Research Information > SEMS > Investigation of Emission Source
Investigation of Emission Source
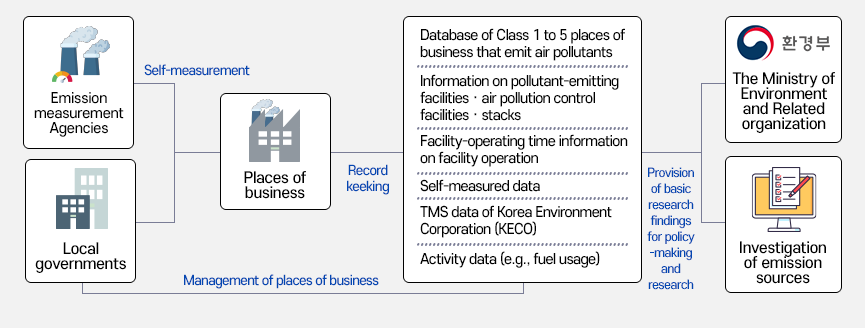
- Data monitored in SEMS are business information, facility information, operational data, self-measured data of emissions, and activity.
- To be more specific, the data include business status, environmental engineer, facility information on air pollutant-emitting facilities · air pollution control facilities · exhaust stacks, operating hours, operational and maintenance data on facilities, and self-measured data and usage.
Data monitored in SEMSⅠ (Information on places of business and their facilities)
| Category | Data | |
|---|---|---|
|
Business Information | General info. | Business registration number, the name of places of business, license number, administrative division, the name of a representative, business type, class 1 to 3 places of business that emit air pollutants, etc. |
| Location | Postal code, phone number, address, area division (Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ), the name of an industrial complex it belongs to, etc. | |
| Stack | Code for places of business that operate TMS, the number of TMS stacks, business history, etc. | |
| Environmental Engineer | Person in charge | Name, position, qualification level, telephone number, mobile number, E-mail, Fax number |
| Agency | Agency’s name, the name of person in charge, project period, telephone number, mobile number, E-mail, Fax number | |
|
Facility Information | Information on Stack | Type (For tele-monitoring system (TMS), TMS number and name, air pollutants measured and monitored online by TMS, etc.), serial number, name, license number, location (latitude and longitude), stack settings, pollutant emissions, classification, the number of holes for gauging pollutants, height and diameter (or cross-sectional area), the list of air pollutants measured and the number of times of measuring emissions |
| Information on air pollution control facilities | Serial number, name, identification number, code, whether to have facilities that prevent air pollutant dispersion, target air pollutants, capacity and efficiency (design vs. actual), year · cost · location of installation, whether to have integrated power meter | |
| Information on air pollutant-emitting facilities |
Serial number, name, identification number, category (large (combustion facilities,
incineration plants, processes and storage facilities) · medium · small), installation
year, etc.
| |
Data monitored in SEMS Ⅱ (Operational Data)
| Category | Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Operational hour | Daily operating time (hours/minutes) by stack, and others | |
| Facility operation | Daily power usage by air pollution control facility, the name of chemicals used, daily chemicals’ usage | |
| Facility maintenance | Maintenance period by control facility, a person in charge of maintenance, maintenance specification | |
| Self-measurement | Meteorological conditions | Weather, temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind direction, wind speed |
| Measurement date and emission gas specification | Measurement date, the method of self-measurement (For laboratories for air pollution, choose the name of laboratory), emission gas speed · temperature · moisture content, actual measurements and standard oxygen concentrations, emission gas flow | |
| Air pollutants | Target air pollutants, concentrations measured, emission standard, devices used for measurement, opinion of environmental engineers on emission inspection | |
| Usage |
| |
Places of business input data to SEMS, and NAIR verifies those data and ask the places of business to complement the data submitted, if necessary.
- * Local governments assist places of business under their jurisdiction in registering their emission data, issue business licenses, and ask for their cooperation.
- * Korea Environment Corporation (KECO) collects the data of places of business that install TMS, and then transfers the data to NAIR.
SEMS Configuration
-
- Emission measurement Agencies
- Local governments
-
Self-measurement
-
Places of business
-
Record keeking
-
- Database of Class 1 to 5 places of business that emit air pollutants
- Information on pollutant-emitting facilitiesㆍair pollution control facilitiesㆍstacks
- Facility-operating time information on facility operation
- Self-measured data
- TMS data of Korea Environment Corporation (KECO)
- Activity data (e.g., fuel usage)
-
Provision of basic research findings for policy-making and research
-
- Management of places of business
- Investigation of emission sources