Research Information
- Particulate Matter
- CAPSS
- SEMS
Home > Research Information > Particulate Matter > Sources of Particulate Matter
Sources of Particulate Matter
Major Air Pollutants (PM)
Particulate Matter (PM) is defined as an ambient fine particle and classified into two major categories according to its particle’s diameter size: PM10 (a particle with diameter less than or equal to 10 ㎛ or less) and PM2.5 (a particle with diameter less than or equal to 2.5 ㎛)
Sources of PM
Sources of PM can be natural and anthropogenic.
- Natural Sources : soil dust, sea salt, pollen, etc.
- Anthropogenic Sources : fumes produced by fossil fuel combustion, car exhaust, fugitive dust produced at construction sites, powdered raw materials and parts used at factories, powdered materials generated during manufacturing processes, fumes produced by incineration, etc.
Composition of PM
Components of PM may differ depending on the region, season, meteorological condition,
etc.
PM consists of compounds (i.e. sulfate, nitrate) that form when air pollutants react in the air,
carbonaceous pollutants produced by fossil fuel consumption, minerals that originate from soil
particles, etc.
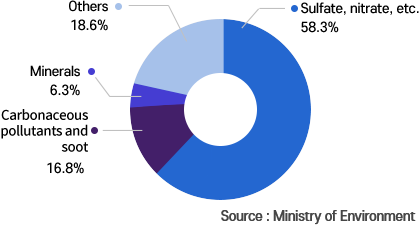
Source : Ministry of Environment
- Sulfate, nitrate, etc. 58.3%
- carbonaceous pollutants 16.8%
- minerals 6.3%
- others 18.6%
Primary PM sources
PM is also divided into primary PM and secondary PM depending on how it forms. Primary PM directly comes from primary PM sources (i.e. exhaust stacks).
- Wildfire
and illegal incineration - Exhaust gas
- Roads,
vacant lands - Factories
- Construction sites
Particulate Matter(PM10)
Source : Ministry of Environment
Secondary PM sources
Secondary PM is formed through the reaction of gaseous pollutants that emit from primary PM sources with other pollutants.
-
- Fossil fuel combustion
- Car exhaust
- Manufacturing process
- Emission of
air polluants -
- Sulfur Oxides(SOx)
- Nitrogen Oxides(NOx)
- VOCs
- Ammonia(NH3)
- Chemical reaction
-
Generation of PM2.5